In this article, we will explore the pros and cons of radiations, presenting a thorough and objective analysis of their benefits and potential risks.
We will delve into advancements in radiation technology rf protection, the role of radiation in medical imaging, and its implications in nuclear energy.
This comprehensive examination aims to provide valuable insights for an audience interested in the various aspects of radiations while maintaining a professional and technical tone.
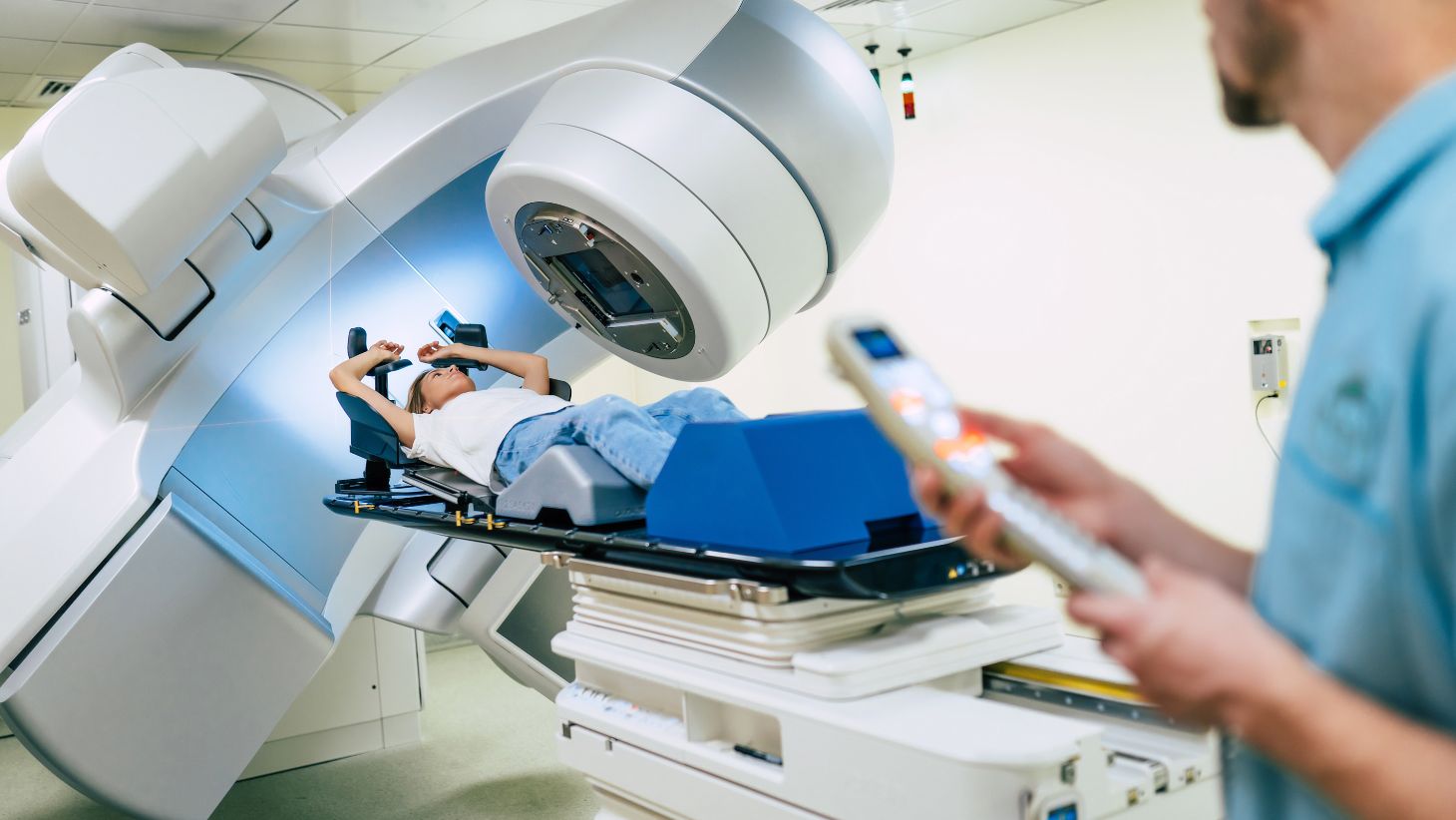
The Benefits of Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy offers significant advantages in the treatment of various cancers, including targeted tumor destruction and improved survival rates. This treatment modality utilizes high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors.
One of the main benefits of radiation therapy is its effectiveness in eradicating cancer cells Lead glass radiation. It can be used as the primary treatment for localized cancers or as an adjuvant therapy following surgery or chemotherapy. The precise targeting of radiation allows for the destruction of cancer cells while minimizing damage to healthy tissues.
Additionally, radiation therapy has been shown to improve survival rates in certain types of cancers, such as breast, lung, and prostate cancer.
Overall, the benefits of radiation therapy in cancer treatment are evident in its ability to effectively target and destroy tumors, leading to improved outcomes for patients.
Advancements in Radiation Technology
Recent advancements in technology have greatly improved the precision and effectiveness of medical procedures involving the use of ionizing energy.
In the field of radiation research, these advancements have revolutionized the way radiation is used in cancer treatment. One significant advancement is the development of image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT), which allows for more accurate targeting of tumors while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues. This technology utilizes real-time imaging techniques to track the movement of tumors during treatment, ensuring that radiation is delivered precisely to the intended area.
Another notable advancement is the use of intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT), which delivers radiation in small, controlled doses from multiple angles, further enhancing treatment accuracy.
These advancements in radiation technology have significantly improved patient outcomes by increasing the effectiveness of cancer treatment while minimizing the risk of side effects.
Potential Risks of Radiation Exposure
Exposure to ionizing energy, particularly in the medical field, necessitates a comprehensive understanding of the potential risks involved to ensure patient safety and well-being. While radiation plays a vital role in diagnosing and treating various medical conditions, it is essential to be aware of the long-term effects it can have on individuals.
Prolonged exposure to ionizing radiation can increase the risk of developing cancer, genetic mutations, and other harmful effects. To mitigate these risks, radiation safety measures are implemented, including the use of shielding devices, proper training for healthcare professionals, and adherence to strict guidelines and protocols.
Regular monitoring and dose optimization techniques further help in minimizing radiation exposure. It is crucial for healthcare professionals to stay updated with the latest research and advancements in radiation safety to provide the best possible care while ensuring patient safety.
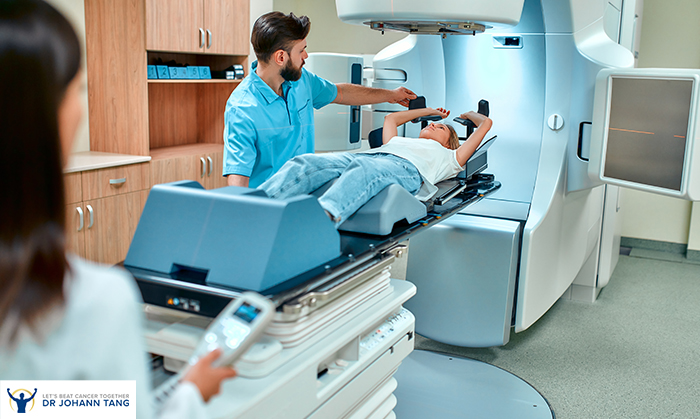
Radiation in Medical Imaging: Pros and Cons
Medical imaging techniques, such as X-rays and CT scans, offer valuable diagnostic information but also present challenges in terms of balancing the benefits and potential risks involved.
These imaging techniques use ionizing radiation, which can have harmful effects on the human body if not properly managed.
One of the main concerns is radiation dosage, as high doses of radiation can increase the risk of developing cancer.
To ensure radiation safety, healthcare professionals must carefully assess the benefits of the imaging procedure against the potential risks. This involves considering factors such as the patient’s age, medical history, and the urgency of the diagnostic information needed.
Additionally, advancements in technology and protocols have helped reduce radiation exposure without compromising the quality of the images.
Continuous monitoring and adherence to established radiation safety guidelines are essential to minimize the risks associated with medical imaging procedures.
The Role of Radiation in Nuclear Energy
Radiation plays a crucial role in the generation of nuclear energy, serving as a source of heat that produces steam to drive turbines and generate electricity.
The use of radiation in this context is carefully regulated to ensure the safety of workers and the environment. The role of radiation safety is to minimize exposure and prevent any potential harm. Various measures are implemented, such as shielding and monitoring systems, to protect workers and the surrounding environment from excessive radiation exposure.
While nuclear energy can provide a significant amount of clean electricity, it also poses potential risks. The impact of radiation on the environment is a concern, as improper disposal of radioactive waste can lead to contamination. It is essential to continuously monitor and manage these risks to ensure the safe and sustainable use of nuclear energy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, radiation therapy offers significant benefits in the treatment of various medical conditions, thanks to advancements in radiation technology.
However, it is important to acknowledge the potential risks associated with radiation exposure.
In the field of medical imaging, radiation has both pros and cons, allowing for accurate diagnosis but also raising concerns about long-term effects.
Moreover, radiation plays a crucial role in nuclear energy, but the associated safety measures must be strictly followed to minimize the potential risks.